
-
Home
- About Us
- Products
- Application scenarios
- Download
- News
Classify- Company News
- Industry News
- FAQ
Industry News
The principle and decoding of the Variable reluctance resolver
2025-12-01Classification of Resolver Sensors
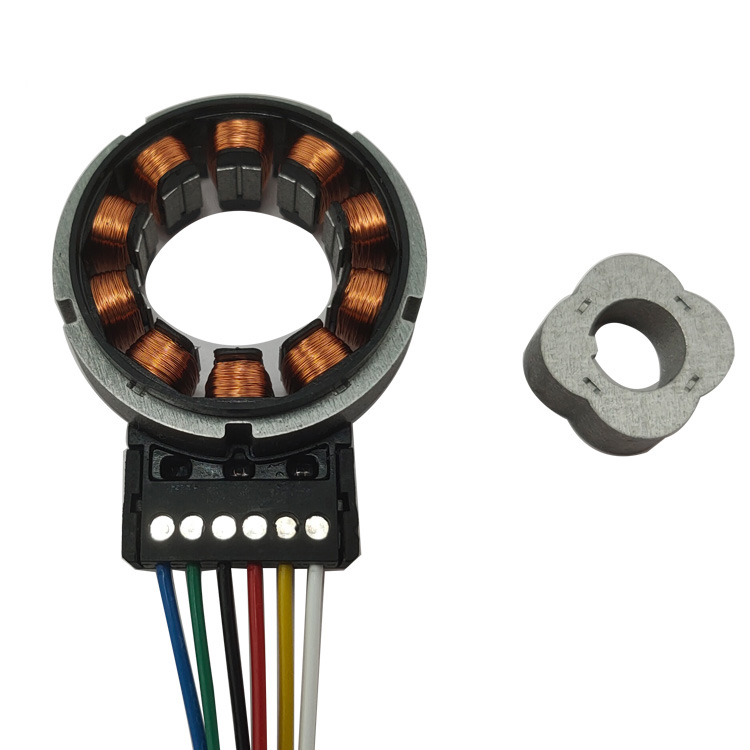
(1) Variable reluctance Resolver

(2) Wound-rotor synchro
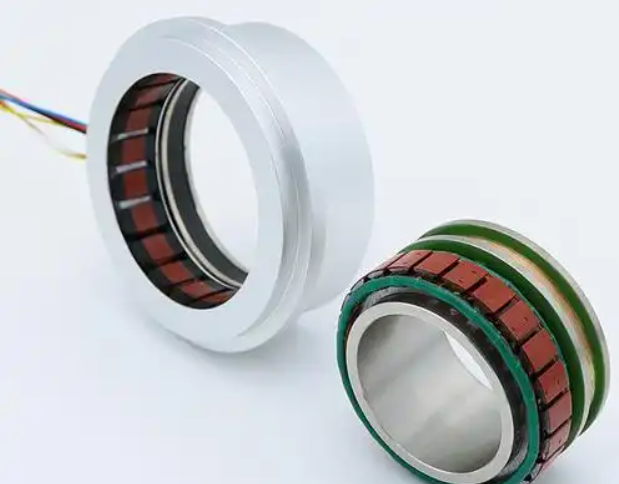

Principle of the Variable reluctance Resolver
The commonly used reluctance resolver changes the coupling between the stator and rotor by altering the air gap reluctance. Both the excitation winding and the output winding are mounted on the stator side. The reluctance rotor, designed with a special profile, rotates synchronously with the rotating object. As the reluctance rotor moves to different positions, the air gap between the stator and rotor changes, causing variations in the air gap permeance. Consequently, the air gap flux fluctuates, leading to changes in the induced electromotive force in the output winding.
The working principle involves altering the air gap length to modify the magnetic reluctance. By designing a resolver rotor with a special contour, the air gap magnetic conductance is ensured to vary as a sine and cosine function, enabling the resolver to output voltages that maintain a sine and cosine relationship with the rotor position angle under high-frequency excitation. The reluctance-type resolver is arranged along a radial line, with the outer contour curve of the resolver rotor exhibiting a wavy shape to ensure the air gap magnetic conductance varies sinusoidally.
The air gap variation ensures the air gap magnetic permeability is sinusoidal, with the permeability Λ varying along the rotor rotation angle θ.
When the input excitation is a constant sinusoidal AC voltage signal U1, the pulsating magnetomotive force F generated by the excitation winding remains constant at any rotor position. Typically, the Sin winding and Cos winding are arranged with slot reverse winding, ensuring the output signals of the two windings are orthogonal. It is essential to maintain mutual isolation between the two windings. The induced voltage magnitudes in the sinusoidal and cosine output windings can be expressed as:
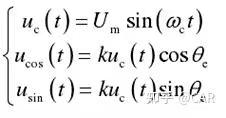
Here, k is a constant value related to the specific parameters of the magnetic reluctance resolver, wc is the carrier angular frequency, and θ is the electrical angle.
Decoding of the reluctance resolver
1) Hardware Decoding Technology
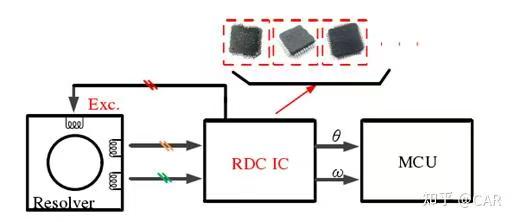
Hardware decoding technology refers to the use of specialized integrated circuit chips, combined with peripheral hardware circuit support, to achieve RDC and obtain rotor position information.
The decoding chip integrates functions such as excitation generation, sampling, and demodulation. The chip generates excitation signals, which are delivered to the resolver input windings via peripheral circuits. The resolver's dual-channel signals are sampled, digitally demodulated, and processed to calculate the rotor angle and speed information. This data is then transmitted to the control loop, enabling stable control of the motor system.
Hardware decoding chip technology is mature and highly reliable, but decoding chips are expensive, accounting for a significant portion of the production costs in electronic control systems. Moreover, the production of RDC chips is primarily controlled by foreign companies, and China currently lacks independent manufacturing capabilities
2) Software Decoding
The extraction of resolver position detection information is achieved by leveraging the abundant peripheral resources and powerful computing capabilities of the main control chip. The main control chip generates excitation signals, which are delivered to the resolver input via a power amplification circuit. The resolver's dual feedback signals are sampled by the main control chip to obtain position information. Software decoding eliminates the need for a decoding chip, simplifying circuit design, saving space and cost, while also offering flexible phase angle observation algorithm selection with a broad range of applications.
Links:
Service Hotline
+86 13923792185
Website:www.micmetering.com
Address:6th Floor, Block B, Area A, Qinghu Science and Technology Park, Longhua District, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province
Copyright © 2025 MIC Metering (Shenzhen) Limited 粤ICP备2025358196号-1 Cookies Policy-
Service Hotline
Service Hotline
+86 13923792185
-
WeChat

-
TOP
Our Cookie Usage Policy
Our website uses cookies and other similar technologies to distinguish you from other users of our website. This helps us provide you with a good experience when you browse our website and allows us to improve our website. For more information, please refer to our Cookie Policy. - About Us







